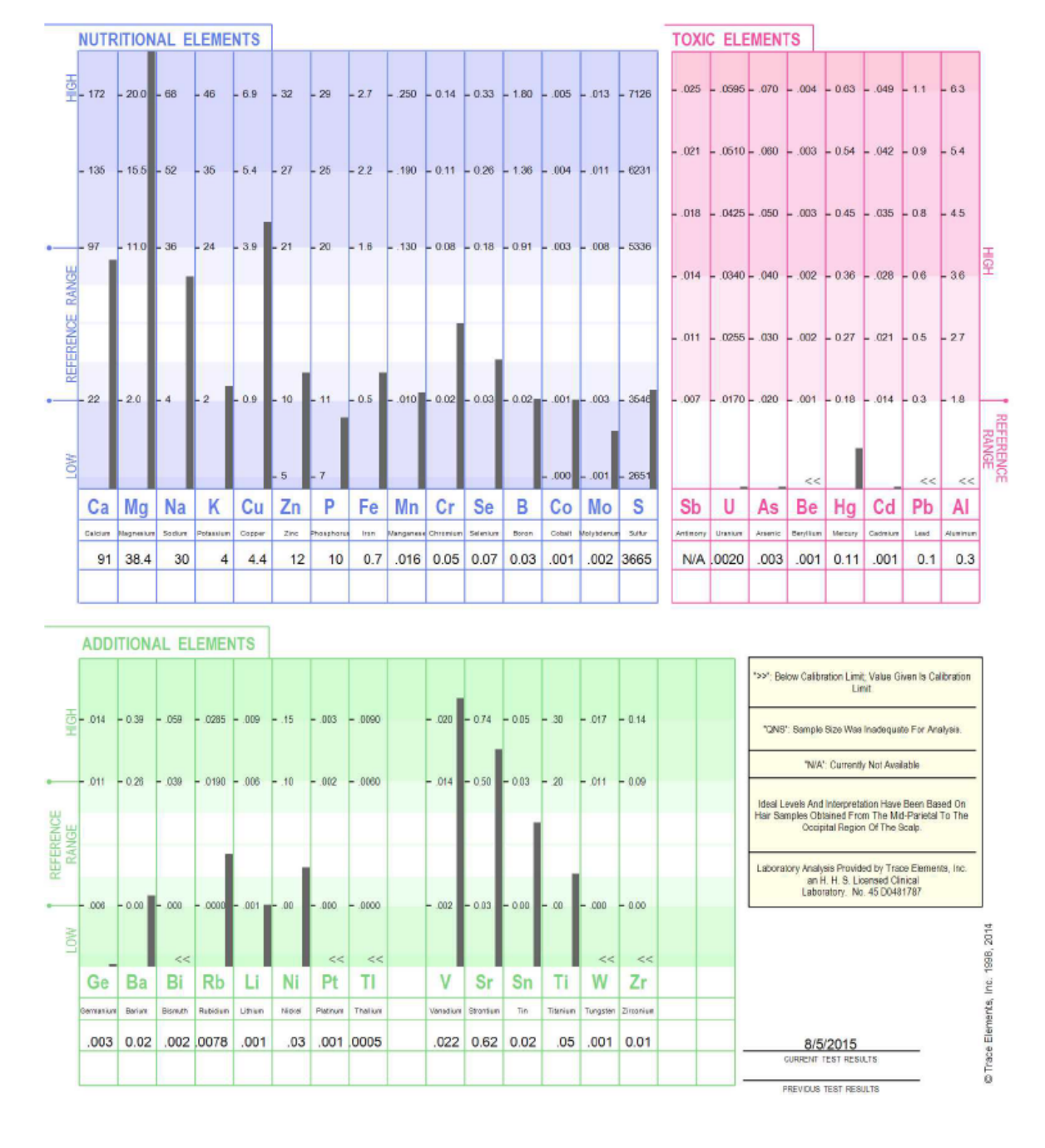
Hair Tissue Mineral Analysis
Hair tissue mineral analysis (HTMA), is an analytical test which measures the mineral content of the hair. The sampled hair, obtained by cutting the first inch and one-half of growth closest to the scalp at the nape of the neck, is prepared in a licensed clinical laboratory through a series of chemical and high temperature digestive procedures. Testing is then performed using highly sophisticated detection equipment and methods to achieve the most accurate and precise results.
Website: HTMA Test
Why Test For Minerals?
Trace minerals are essential in countless metabolic functions in all phases of the life process.
Zinc is involved in the production, storage, and secretion of insulin and is necessary for growth hormones.
Magnesium is required for normal muscular function, especially the heart. A deficiency has been associated with an increased incidence of abnormal heart conditions, anxiety, and nervousness.
Potassium is critical for normal nutrient transport into the cell. A deficiency can result in muscular weakness, mild depression, and lethargy.
Excess sodium is associated with hypertension, but adequate amounts are required for normal health
In the words of the late author and noted researcher, Dr. Henry Schroeder, trace elements (minerals) are "...more important factors in human nutrition than vitamins. The body can manufacture many vitamins, but it cannot produce necessary trace minerals or get rid of many possible excesses."
What can cause a mineral imbalance?
There are many factors to take into consideration, such as:
Diet - Improper diet through high intake of refined and processed foods, alcohol and fad diets can all lead to a chemical imbalance. Even the nutrient content of a "healthy" diet can be inadequate, depending upon the soil in which the food was grown or the method in which it was prepared.
Stress - Physical or emotional stress can deplete the body of many nutrients while also reducing the capability to absorb and utilize many nutrients.
Medications - Both prescription and over-the-counter medications can deplete the body stores of nutrient minerals and/or increase the levels of toxic metals. These medications include diuretics, antacids, aspirin and oral contraceptives.
Pollution - From adolescence through adulthood the average person is continually exposed to a variety of toxic metal sources such as cigarette smoke (cadmium), hair dyes (lead), hydrogenated oils (nickel), anti-perspirants (aluminum), dental amalgams (mercury and cadmium), copper and aluminum cookware and lead-based cosmetics. These are just a few of the hundreds of sources which can contribute to nutrient imbalances and adverse metabolic effects.
Nutritional Supplements - Taking incorrect supplements or improper amounts of supplements can produce many vitamin and mineral excesses and/or deficiencies, contributing to an overall biochemical imbalance.
Inherited Patterns - A predisposition toward certain mineral imbalances, deficiencies, and excesses can be inherited from parents.
Can vitamin requirements be determined from a mineral test?
Minerals interact not only with each other but also with vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Minerals influence each of these factors, and they, in turn, influence mineral status. Minerals act as enzyme activators, and vitamins are synergistic to minerals as coenzymes. It is extremely rare that a mineral disturbance develops without a corresponding disturbance in the synergistic vitamin(s). It is also rare for a disturbance in the utilization or activity of a vitamin to occur without affecting a synergistic mineral(s). For example, vitamin C affects iron absorption and reduces copper retention. Boron and iron influence the status of vitamin B2. Vitamin B2 affects the relationship between calcium and magnesium. Vitamin B1 enhances sodium retention, B12 enhances iron and cobalt absorption, and vitamin A enhances the utilization of zinc while antagonizing vitamins D and E. Protein intake will affect zinc status, etc. Therefore, evaluating mineral status provides good clues about vitamin status and requirements.
Continuing research at Trace Elements involves the recognition of many synergistic and antagonistic interrelationships between minerals and vitamins.